+86 13816508465
Pump Knowledge
Sep. 24, 2024

The motor is the heart of a water pump, and its temperature rise is a critical factor in determining the pump's overall performance and lifespan. Ensuring that the motor's temperature remains within the recommended range is essential for maximizing the efficiency, reliability, and longevity of your water pumping system.
What is Motor Temperature Rise?
Motor temperature rise refers to the difference between the motor's operating temperature and the ambient temperature. When a motor is running, it generates heat due to the electrical and mechanical energy being converted into work. If this heat buildup is not effectively dissipated, it can lead to an unacceptable rise in the motor's temperature.
Note: The unit of temperature rise is K (Kelvin), where 1 K = Δ1°C, making it a variable unit. Strictly speaking, the °C unit is used to represent a fixed temperature, making it a constant unit.
Disadvantages of High Motor Temp. Rise
Allowing the motor temperature to rise too high can have serious consequences for the pump's performance and durability:
1. Damage to Insulation:
Excessive heat can degrade the insulation on the motor's windings, increasing the risk of short circuits and electrical failures.
2. Bearing Failure:
High temperatures can cause premature wear and failure of the motor's bearings, leading to mechanical issues and potential seizure of the pump.
3. Reduced Efficiency:
As the motor temperature rises, its electrical resistance increases, resulting in higher energy consumption and lower overall pump efficiency.
4. Shortened Lifespan:
Prolonged exposure to high temperatures can significantly shorten the motor's lifespan, leading to more frequent pump replacements and increased maintenance costs.
Measures to Control Motor Temp. Rise
From the view of a pump manufacturer, the most important part to control a motor temp.rise is from the original design and production process. Choose a supplier with better motor production and good temp.control could avoid the problems in a largest extent.
Here are tips from choosing a better motor ahead:
Better Cooling Design:
Optimize the motor's cooling system, such as by using larger cooling fans, better airflow paths, or even water cooling motors, to enhance heat dissipation.
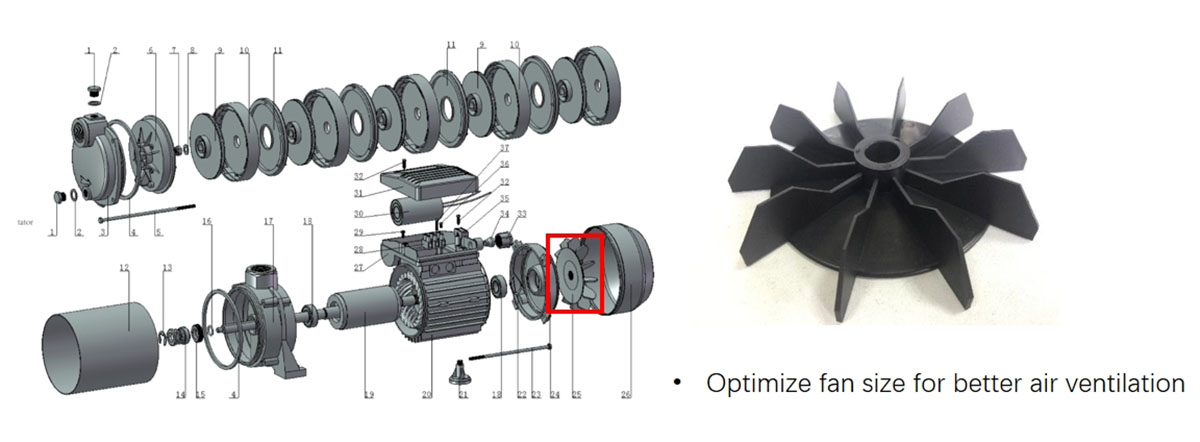
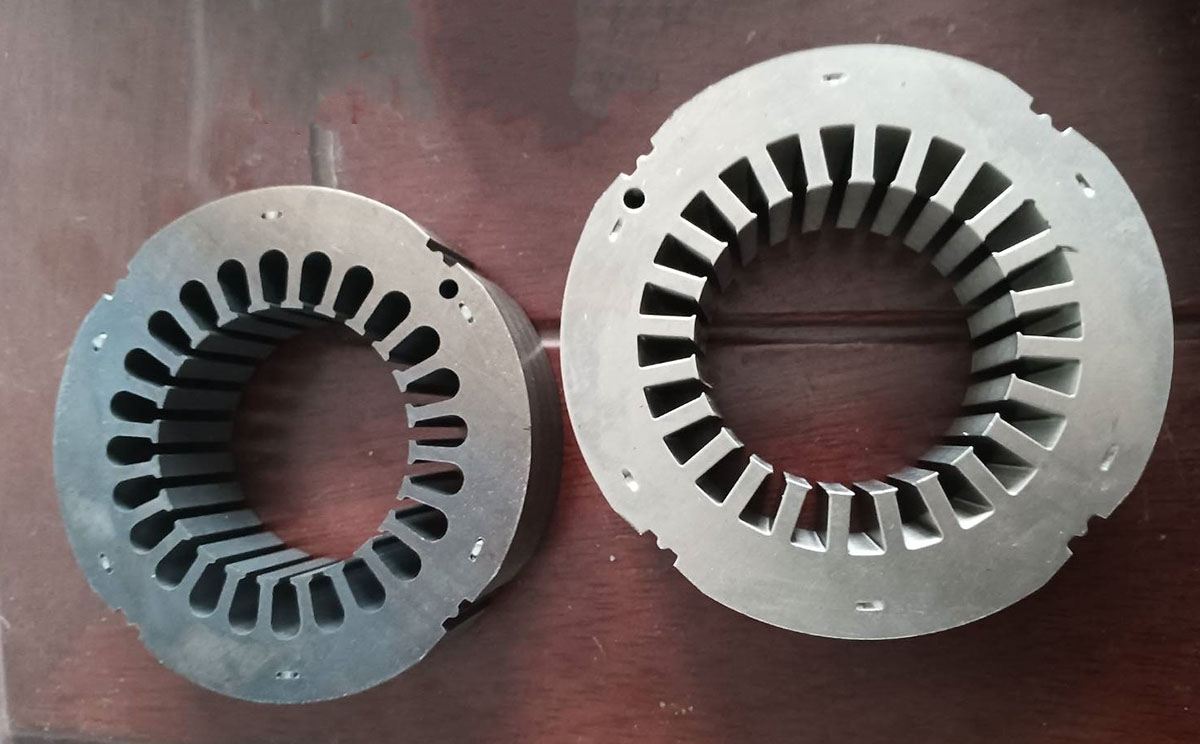
Select Appropriate Materials:
Choosing the right steel for motor stators and rotors is crucial for performance and durability, especially in high-temperature situations. Cold-rolled steel 800 is a high-quality option that offers excellent magnetic properties, allowing for greater efficiency and the ability to withstand higher temperatures without performance loss. This steel also helps reduce noise and vibration in operation. On the other hand, strip steel Q195 is a more cost-effective choice but has lower heat tolerance and efficiency, making it suitable for less demanding applications.

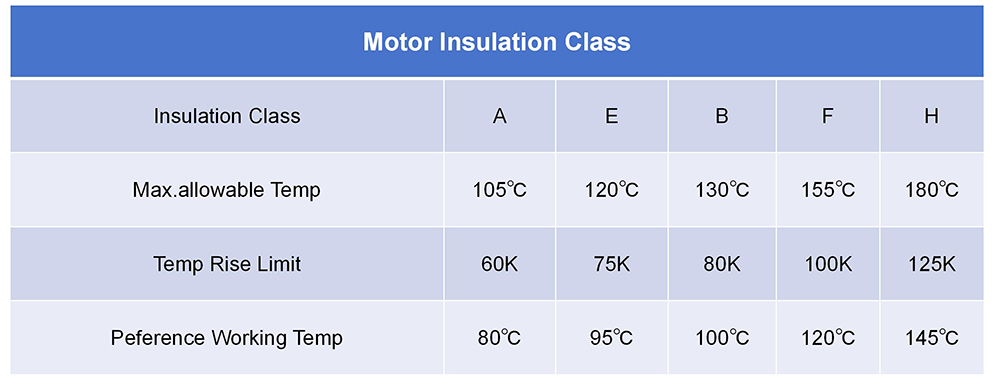
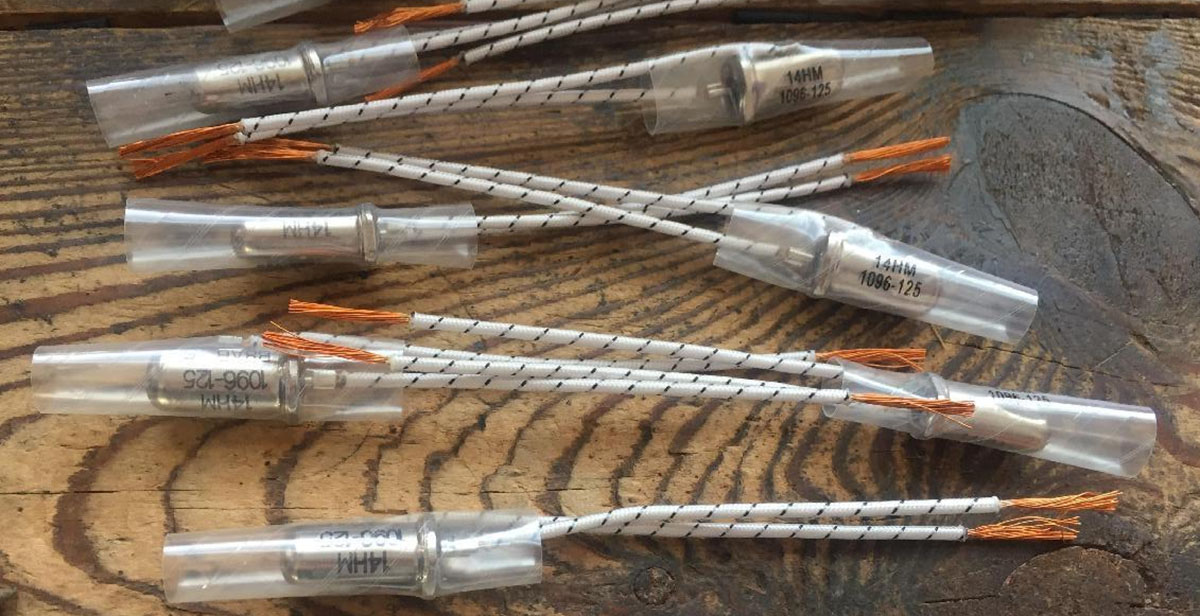
Higher-Grade Insulation:
Choose motor with a higher insulation class, which can withstand higher temperatures without degradation. The larger grade, the higher temp.rise limit which extends the service time of a motor under severe conditions.
Common motor insulation and the related temp. As below:
Install Thermal Protector:
Install temperature sensors into the motor design to detect and respond to any potential overheating issues. Attention that in specific market, the degree of thermal protector’s cut in temperature should be adjusted accordingly to suit different market needs.

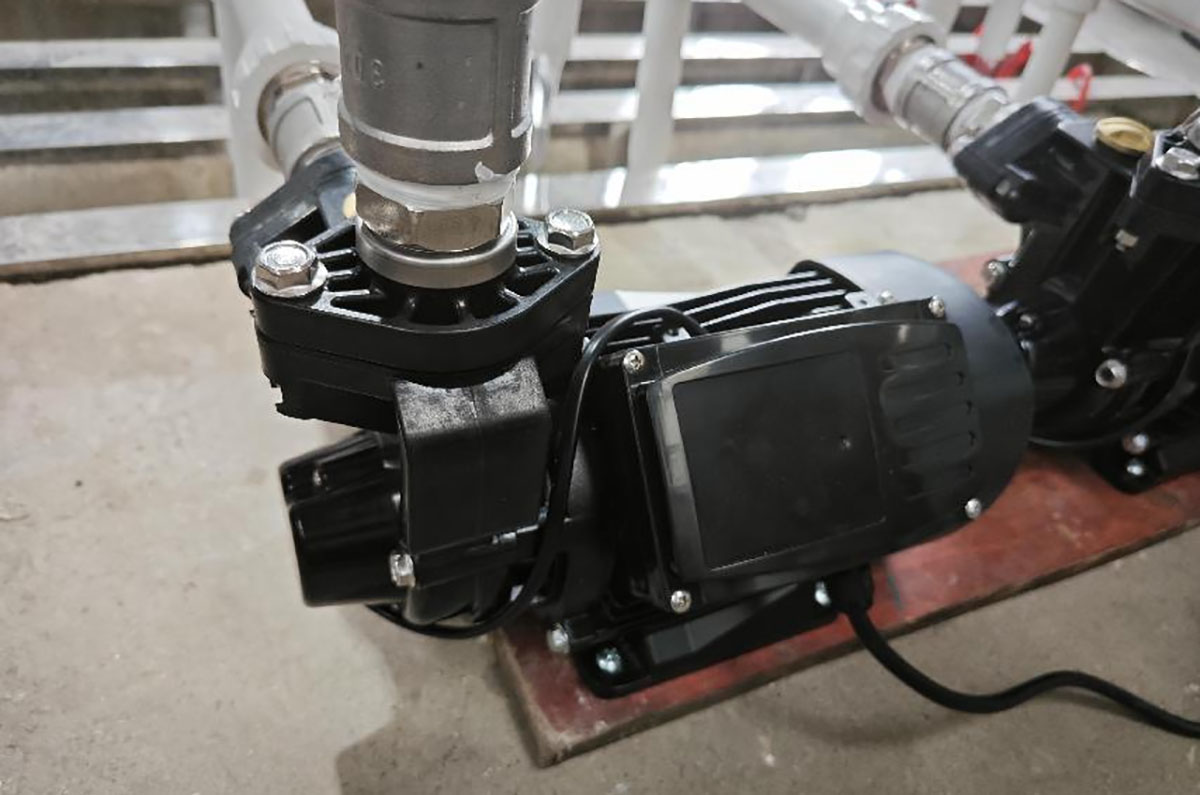
Conduct Rigorous Testing:
Perform thorough testing of the motor's temperature rise and thermal performance across various operating conditions to ensure it meets the required specifications. Typically, a new pump should undergo a durability test of over 1,500 hours. This extensive testing ensures that all pump components fit together correctly and operate consistently, ultimately guaranteeing stable and reliable performance.

To ensure optimal pump performance and longevity, some other measures on site can also be helpful.
Proper Ventilation:
Ensure that the pump is installed in a well-ventilated area, allowing for adequate airflow around the motor. This helps dissipate the heat generated during operation.
Regular Maintenance:
Regularly inspect and clean the pump and motor to remove any dirt, debris, or obstructions that can impede airflow and contribute to heat buildup.
Thermal Protection:
Install thermal protection devices, such as overload relays or thermistors, to automatically shut down the pump if the motor temperature exceeds safe limits.
Load Monitoring:
Monitor the pump's operating conditions, such as flow rate, pressure, and power consumption, to identify any changes that could indicate a rise in motor temperature. DONOT run the pump overhead for a long period which could cause great damage in motor operation.
By proactively pay attention to the motor's temperature rise, you can help ensure the reliable and efficient operation of your water pumping system, minimize downtime, and extend the overall lifespan of your equipment.
Address
No.17 XeDa Jimei Ind. Park, Xiqing Economic Development Area, Tianjin, China
Telephone
+86 13816508465
QUICK LINKS