+86 13816508465
Pump Knowledge
Mar. 18, 2025

1. Applications of Hot Water Circulation Pumps
Hot water circulation pumps are used in various systems to circulate hot water efficiently. Here are the main applications:

a. Boiler Systems
Function: The pump helps circulate heated water from the boiler to radiators, underfloor heating systems, or other heat exchangers.
Installation: Typically installed near the boiler's outlet to ensure the pump can circulate water effectively through the heating system.
Precautions: Ensure the pump's flow rate and pressure meet the system's requirements. Consider using corrosion-resistant materials for both the pump and connected pipes to prolong lifespan.
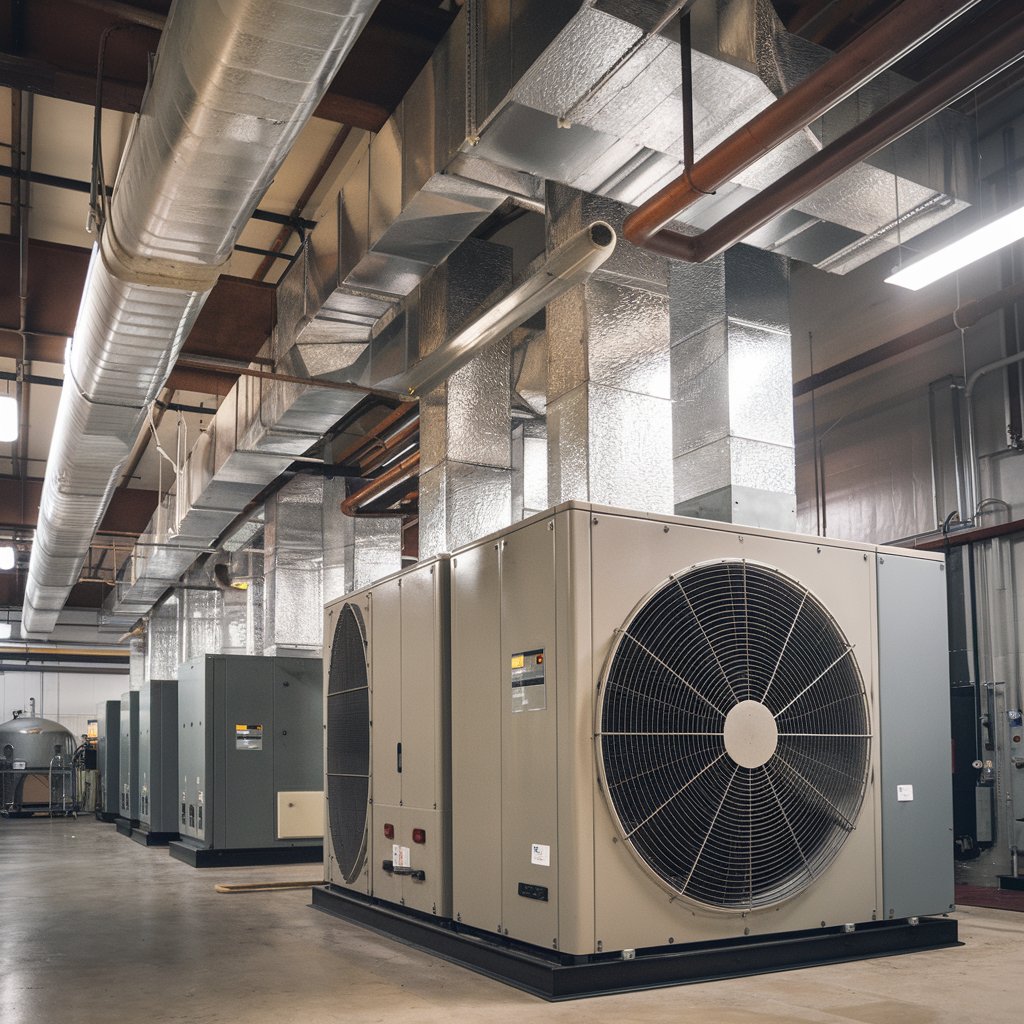

b. HVAC Systems
Function: In HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) systems, the pump circulates hot water for heating or cooling purposes, distributing it through air handlers, radiators, or fan coils.
Installation: The pump is installed between the heating source (such as a boiler) and the heat distribution system.
Precautions: Choose a pump that matches the flow and pressure requirements of the HVAC system. Proper insulation of the pipes can also improve system efficiency.
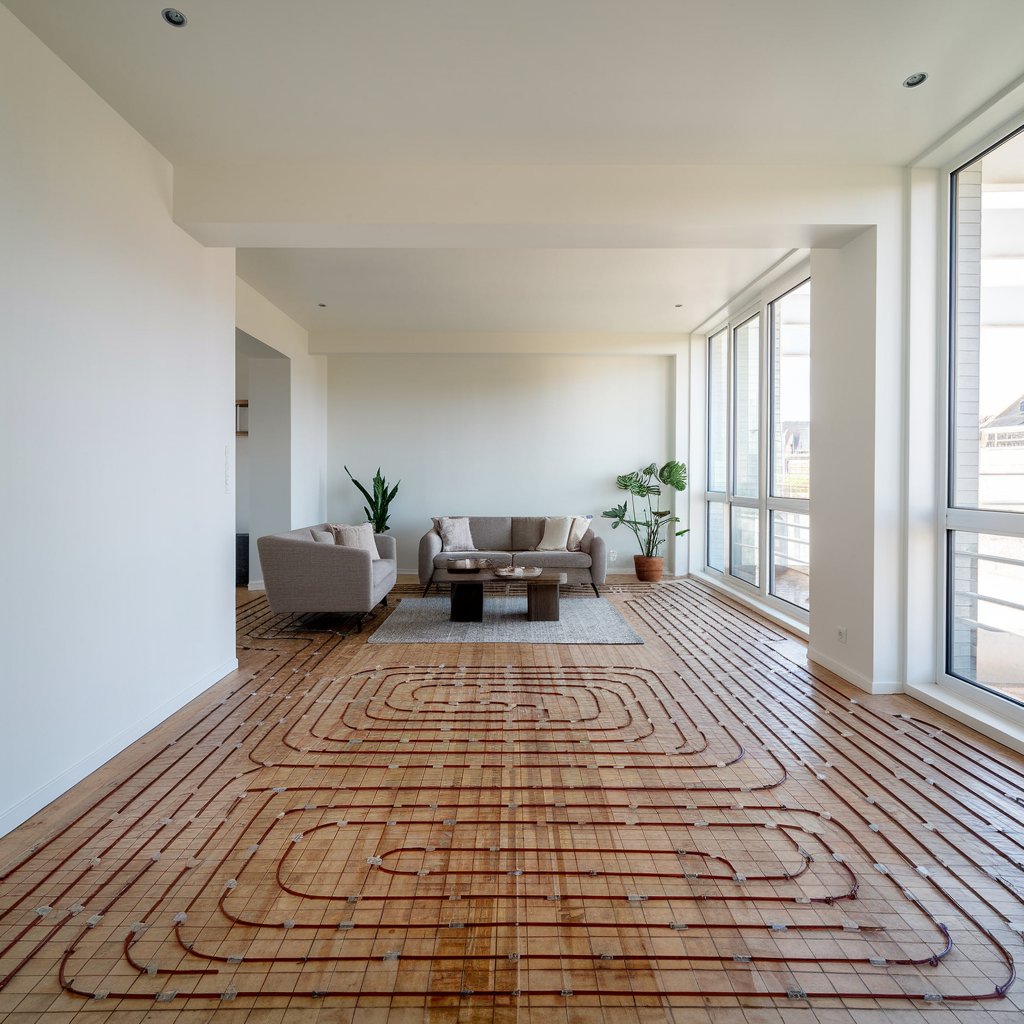

c. Underfloor Heating Systems
Function: A circulation pump is vital for maintaining consistent water flow through the underfloor heating loops, ensuring even heat distribution across the floor.
Installation: Pumps are typically installed in the loop circuit, between the manifold and the underfloor heating pipes.
Precautions: Ensure a constant flow rate to avoid uneven heating. Pay attention to the installation height—pumps should be installed at the lowest point to ensure water circulation.
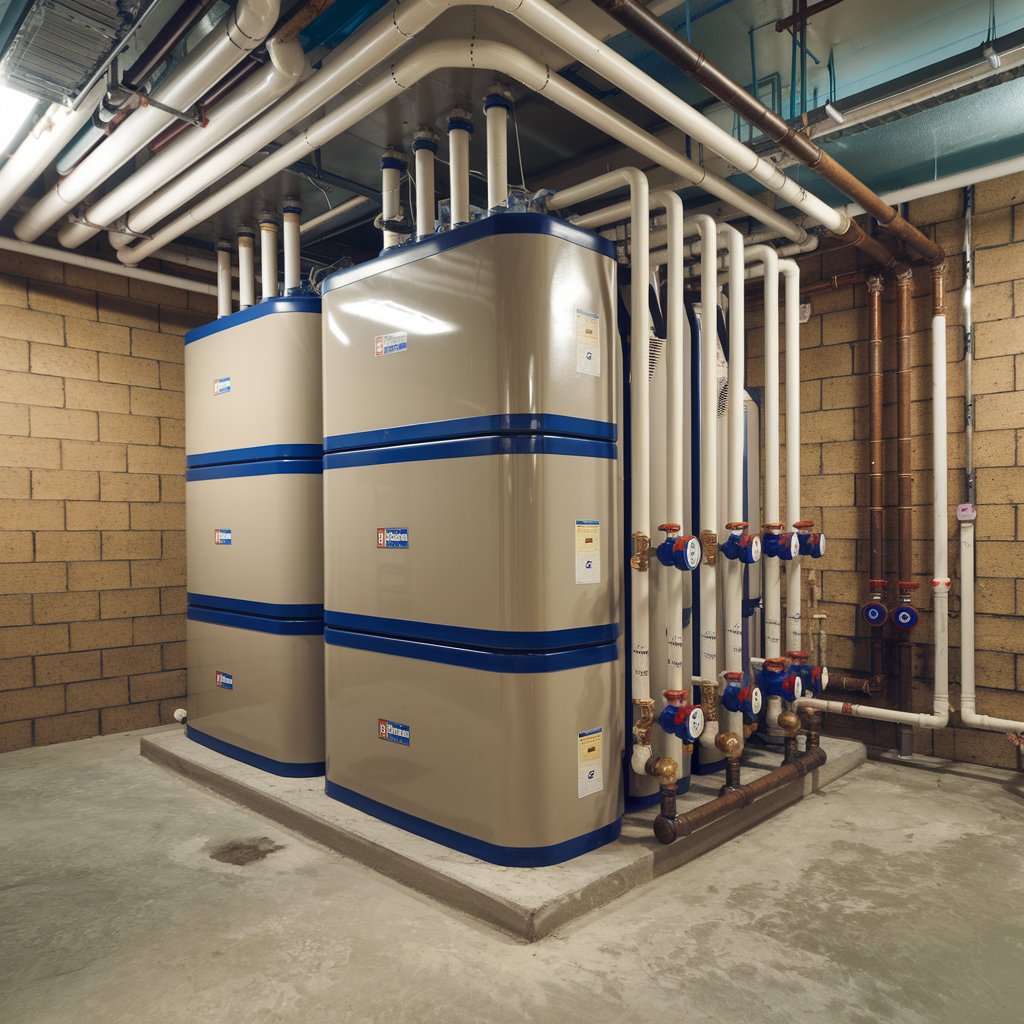

d. Water Heater Systems
Function: In domestic or commercial water heaters, the pump ensures hot water circulates through the system, providing instant hot water at the taps.
Installation: The pump is placed between the water heater and the water supply lines to keep hot water moving through the system and prevent heat loss.
Precautions: Ensure the pump is compatible with your water heater's output. Proper pipe insulation is necessary to reduce heat loss.
2. Installation Methods
The installation of a hot water circulation pump depends on the system it serves. Below are general installation guidelines:
a. Pump Direction (Inlet/Outlet)
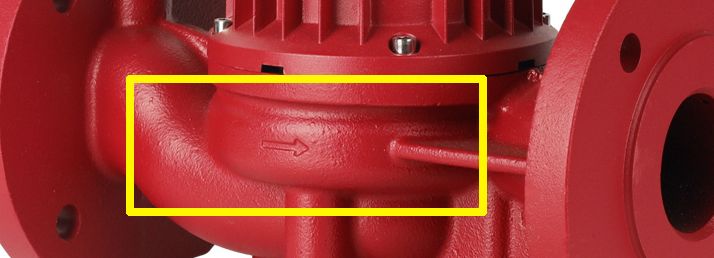
Always ensure the pump's inlet and outlet are properly aligned with the flow direction of the system.
Inlet: The inlet should be connected to the hot water supply line from the heat source (e.g., boiler).
Outlet: The outlet should lead to the heat distribution system (radiators, underfloor pipes, etc.).
b. Ventilation (Air Bleeding)
Air Venting: Circulation systems should be purged of air after installation. Air in the system can cause inefficiency and noise.
Install air vents or use automatic air vents in the pump system to prevent airlocks, ensuring smooth operation.
c. Horizontal vs. Vertical Installation
Horizontal Installation: Commonly used when space is limited. Ensure the pump is installed with the shaft in a horizontal position to avoid mechanical wear.
Vertical Installation: Some pumps are designed for vertical installation, typically when space allows or when required by the system design. Ensure the pump's orientation aligns with the manufacturer’s instructions.
d. Pump Protection
Strainer/Filter: Install a strainer or filter at the pump's inlet to protect it from debris that could damage the impeller or motor.
Thermal Protection: Many pumps come with built-in thermal overload protection. If the pump doesn't include this feature, consider installing a separate thermal protector to prevent overheating.
Pressure Relief Valve: For systems with fluctuating pressure, install a pressure relief valve to protect the pump and the system from excessive pressure buildup.
3. Precautions During Installation
Here are key points to keep in mind during the installation process:
a. Correct Sizing of the Pump
Ensure that the pump's flow rate and pressure capabilities match the requirements of the system it is servicing. Too large or too small a pump can result in inefficiency or system failure.
b. Electrical Connections
Always follow the manufacturer's wiring diagram when connecting the pump to the power supply. For safety, ensure proper grounding and use the correct voltage and amperage as specified in the pump's manual.
c. Pipework
Use high-quality, corrosion-resistant pipes and fittings, especially when dealing with hot water. Copper or stainless steel pipes are often recommended for their durability.
Ensure all pipe joints are sealed correctly to prevent leaks. Tighten connections properly but avoid overtightening, which can damage the threads.
d. Pump Orientation
The pump’s motor should typically be mounted in a horizontal position unless specified otherwise by the manufacturer. Improper alignment can result in mechanical wear and reduced pump life.
Ensure that the pump is securely mounted to avoid vibrations that could lead to noise or damage.
e. System Testing
After installation, test the system by running the pump for several minutes to ensure proper circulation and detect any leaks or noise.
Use a flow meter and pressure gauge to verify that the system is operating within the required specifications.
4. Tools Needed for Installation
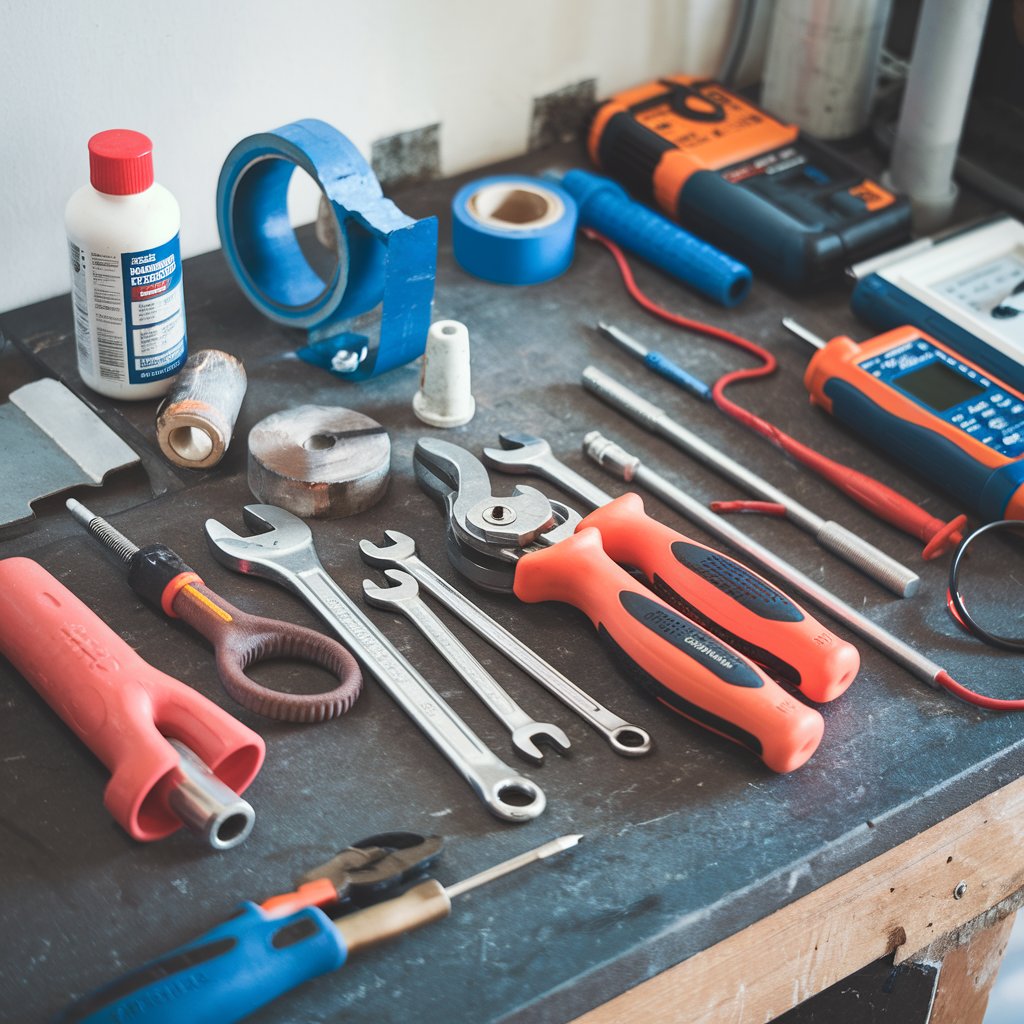

Below are some essential tools you may need when installing a hot water circulation pump:
Pipe Cutting Tools: Pipe cutters or hacksaws for cutting pipes to the correct length.
Wrenches and Torque Wrenches: To tighten pipe fittings and the pump connections securely.
Plumbing Sealant or Thread Tape: To seal threaded connections and prevent leaks.
Pipe Bender: If you need to bend pipes for tight spaces, ensure the bend is smooth to prevent blockages.
Screwdrivers: For attaching brackets or securing the pump in place.
Multimeter and Electrical Tools: To check the pump’s electrical connections and ensure the motor is functioning correctly.
Flow Meter and Pressure Gauge: To verify system flow and pressure.
5. Maintenance and Long-Term Care
Regular Inspection: Inspect the pump regularly for any signs of leaks, noise, or unusual vibrations.
Lubrication: Some pumps require periodic lubrication to keep moving parts running smoothly. Refer to the manufacturer's maintenance guide.
Cleaning: Keep the pump and system free from debris. Clean the filter or strainer regularly to ensure optimal performance.
By following this guide, you can ensure the safe and efficient installation of your hot water circulation pump. If you need further details or encounter specific issues, consult the manufacturer's manual or contact a professional plumber for assistance.
Here is another installation tips we provided in 22 years:https://www.streampumps.com/pump-solutions/9.html
Address
No.17 XeDa Jimei Ind. Park, Xiqing Economic Development Area, Tianjin, China
Telephone
+86 13816508465
QUICK LINKS